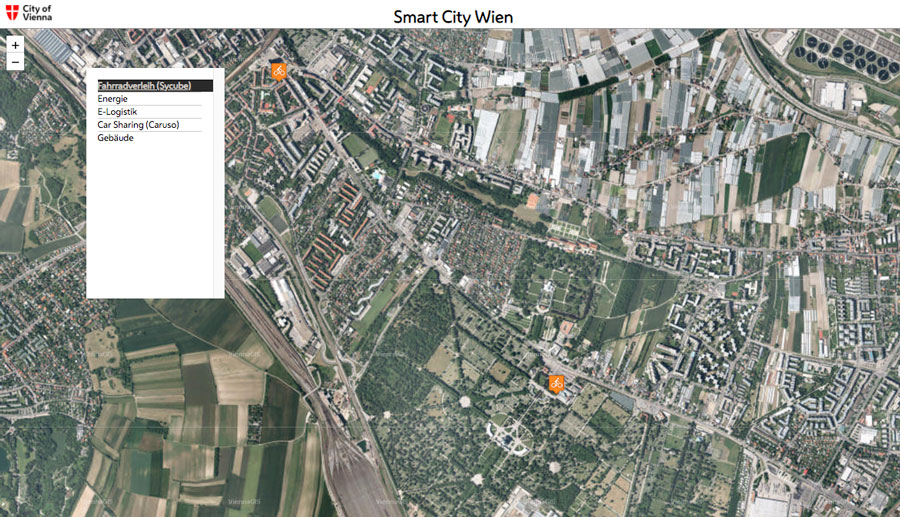
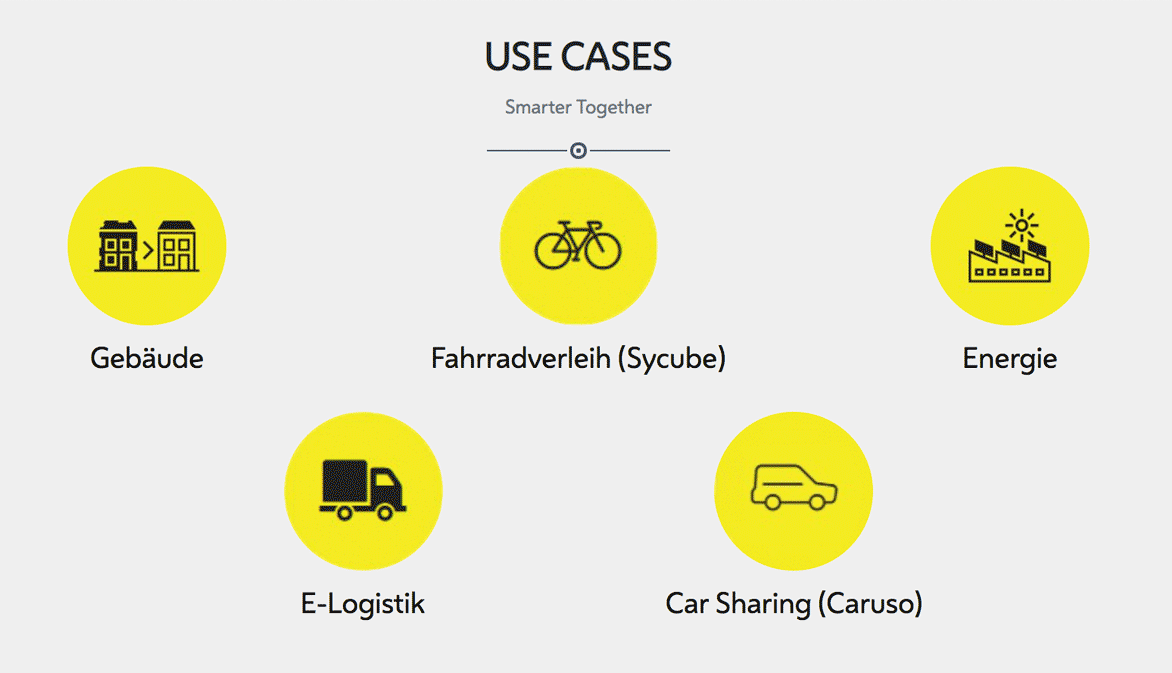
The project provides a citywide infrastructure for capturing and using data for various Smart City projects in fields like energy, buildings, and mobility.
In their joint EU project “Smarter Together”, the cities of Lyon, Munich and Vienna collected large amounts of data on the topic of Smart City – data captured by sensors, data on buildings, and environmental data. As a next step, the data is published on an urban data platform based on open standards.
A platform for smart city data
Various data, e.g. from the Internet of Things (IoT) or real-time data, are available to be used by the public, businesses, and the scientific community. The data is visualised and directly accessible to anyone who, for example, wants to check the location of cars or bikes available via mobility sharing platforms, or directly read the temperature measured by a sensor.
At the same time, businesses can benefit from a common platform for data collection and data exchange between public and private partners.
Accessibility and transparency
The urban data platform smartdata.wien uses a platform called FIWARE , based on open standards and open source software. This ranges from the back-end software, using open-stack and FIWARE components, to specific applications for visualisation or calculation.
The City of Vienna is a member of the Open & Agile Smart Cities (OASC) network and complies with the Minimum Interoperability Mechanisms (MIMs) on its Urban Data Platform.
The MIMs defined by the OASC are a constantly evolving set of technical mechanisms selected from a baseline of global best practices, driven by implementation in the network’s member cities, and incorporated into standardisation activities such as ETSI, ISO and ITU.
The Vienna Business Agency is in charge of coordinating the FIWARE community.
This post is also available in: German